API Standard 600 Overview – Flanged & Butt-Weld Steel Gate Valves
API Standard 600 defines the design, materials, testing, and inspection requirements for bolted bonnet steel gate valves used in oil, gas, petrochemical, and power industries. These valves provide reliable on/off isolation in high-pressure and high-temperature systems, ensuring safety and durability. Understanding API 600 helps engineers, project managers, and procurement teams select and maintain valves that meet strict industry standards.
- Introduction
- Understanding Gate Valve Types
- Materials and Construction
- End Connections and Piping Integration
- Design Features and Safety Considerations
- Testing, Inspection, and Quality Checks
- Marking, Documentation, and Certification
- Practical Guidelines for Valve Selection and Use
- Annexes Simplified
- Conclusion
Introduction
API Standard 600 specifies the requirements for a heavy-duty series of bolted bonnet steel gate valves, primarily intended for petroleum refining and related industries where corrosion, erosion, and severe service conditions demand robust construction. The standard ensures valves are designed to deliver reliable shutoff performance while accommodating full port openings, heavy wall sections, and large stem diameters.
Key design features covered under API 600 include:
- Bolted bonnet construction
- Outside screw and yoke (OS&Y) design
- Rising stems with non-rising handwheels
- Single or double gate configurations
- Wedge or parallel seating options
- Metallic seating surfaces
- Flanged or butt-welding end connections
The standard applies to gate valves in nominal pipe sizes ranging from DN 25 (NPS 1) up to DN 1050 (NPS 42), and for pressure class designations 150 through 2500. By adhering to these requirements, manufacturers provide valves capable of safe operation in high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive environments. Where the API Monogram is applied, additional manufacturing and quality requirements of Annex A are mandatory.
Understanding Gate Valve Types
Gate valves are designed to control the flow of fluids by fully opening or closing the passage. Choosing the correct type is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. API 600 covers several configurations, each suited for specific applications.
Rising Stem (OS&Y) vs Non-Rising Stem: Rising stem valves clearly indicate whether the valve is open or closed, making them ideal for frequent operation. Non-rising stem valves have a compact design, suitable for tight spaces where vertical stem movement is restricted.
Disc Designs – Wedge vs Parallel: Wedge-type discs provide tight shutoff and are commonly used in high-pressure applications. Parallel discs, often with resilient or hard-faced seats, allow easier operation in larger sizes or high-temperature systems.
Bonnet Types – Bolted vs Pressure Seal: Bolted bonnet valves are standard and allow easy maintenance, while pressure seal bonnets are used in higher pressure or temperature conditions, providing enhanced sealing and safety.
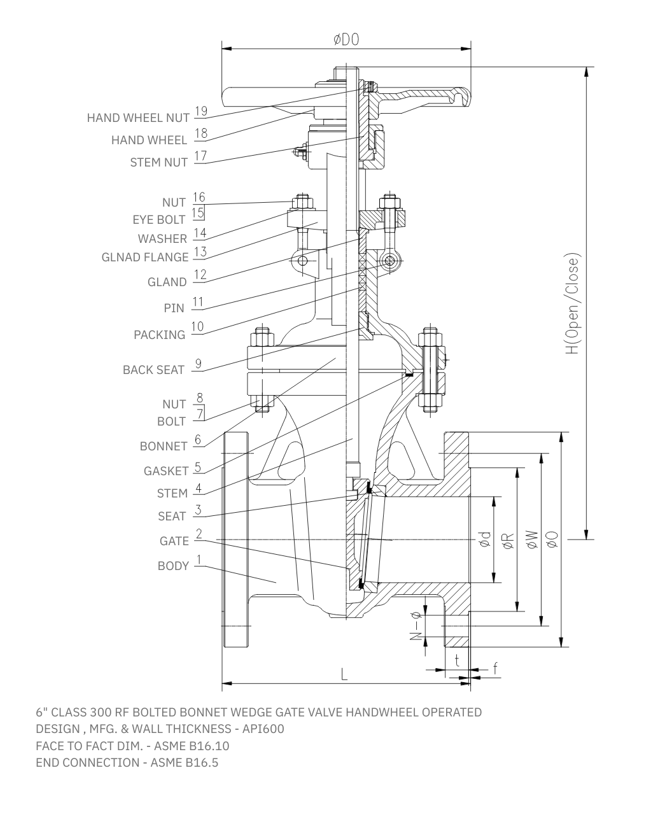
Materials and Construction
Selecting the right materials is critical for valve performance, safety, and longevity. API 600 specifies suitable materials for the body, bonnet, stem, trim, and sealing components based on pressure, temperature, and fluid compatibility.
Body and Bonnet Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels are commonly used depending on operating conditions. High-temperature or corrosive services often require alloy materials to ensure structural integrity and corrosion resistance.
Sealing Materials: Seals and gaskets must withstand system temperatures and pressures without leakage. Choices include graphite, PTFE, and other high-performance elastomers depending on chemical compatibility and temperature limits.
Valve Trim and Seat Selection
API 600 defines multiple trim types that combine the disc, seat, stem, and backseat materials. While the standard provides detailed tables, the key practical takeaway is understanding the number of trim types, their materials, and how to select the correct one for your application.
Number of Standard Trims: API 600 specifies 21 standard trim combinations in Table 8 (Nominal Seating Surface, Stem and Backseat Bushing or Weld-deposit Materials and Hardness). Each trim specifies compatible disc, seat, and stem materials suitable for different pressures, temperatures, and fluid types.
Using Trim Tables Practically:
- Identify your operating conditions: fluid type, temperature, pressure, and potential erosion/corrosion.
- Check trim compatibility: Select a trim type that matches the body material and operating conditions.
- Seat and disc pairing: Ensure the seat material is compatible with the disc type (e.g., hard-faced seats for erosive services, soft seats for lower pressures).
- Stem considerations: Choose a stem material and hardness that resists wear, galling, and cyclic loading for your service.
Practical Example: For a high-temperature steam application, you might select a WC6 alloy steel body with Trim 5, which includes a hard-faced Stellite seat and an F6a stem. This ensures tight shutoff, wear resistance, and long service life.
Important Note on "Trim" vs. "Trim Number": API 600 makes a clear distinction:
Trim: The combination of the stem, disc (closure member), and seat ring seating surfaces. It is defined by the materials and the method of attachment.
Trim Number: A number from Table 8 used to designate a specific, standardized combination of materials for these parts.
End Connections and Piping Integration
API 600 primarily covers bolted bonnet steel gate valves with flanged ends. The standard specifies that body end flanges for valves up to DN 600 (NPS 24) shall comply with the dimensional requirements of ASME B16.5. For larger sizes, flanges must meet ASME B16.47 Series A or B as specified by the purchaser. Raised face flanges are provided unless otherwise specified, and flange facing finishes may be adjusted per purchaser requirements.
Face-to-face dimensions for flanged valves are defined by ASME B16.10 or ISO 5752. Flanges are generally cast or forged integral with the valve body, though welded attachment is permitted when approved by the purchaser. When welding is used, full penetration butt-welding is required, following ASME B31.3 or ISO 15649 standards, including weld quality criteria, procedure qualifications, and heat treatment as applicable.
Butt-welding ends are permitted for valve sizes greater than NPS 2 and must conform to ASME B16.25 for the specified bore. Valves DN 50 (NPS 2) and smaller follow API 602 requirements. Conversion of a flanged valve to a butt-welding valve is only allowed by agreement between the purchaser and manufacturer. Material requirements for carbon steel welding ends include a maximum carbon content of 0.23% and a carbon equivalent (CE) not exceeding 0.43.
By adhering to these dimensional and material requirements, valves maintain proper alignment, ensure leak-tight integration with piping, and meet project-specific operational and safety standards.
Design Features and Safety Considerations
API 600 incorporates design features that enhance safety, reliability, and operational efficiency. Understanding these features helps engineers select valves that meet both performance and regulatory requirements.
Anti-Blowout Stems: These stems prevent the valve disc from being ejected under pressure, protecting personnel and equipment. They are a critical safety feature for high-pressure applications.
Fire-Safe Design: Valves designed to meet fire-safe requirements (such as API 607 or API 6FA) ensure that sealing elements maintain integrity during fire exposure, reducing the risk of leakage and catastrophic failures.
Extended Bonnet: Extended bonnets are used for high-temperature or cryogenic services, allowing thermal expansion and protecting the actuator and packing from extreme temperatures. This design ensures reliable operation in demanding conditions.
Incorporating these design features ensures valves operate safely, reduce maintenance risks, and maintain system integrity under extreme operating conditions.
Testing, Inspection, and Quality Checks
Proper testing and inspection are essential to ensure valves meet operational requirements and maintain safety. API 600 specifies procedures that verify mechanical integrity, sealing performance, and compliance with project specifications.
Hydrostatic Shell Test: This test checks the valve body for leaks and strength by applying water or another incompressible fluid at pressures above the maximum operating pressure. It ensures the valve can safely withstand system pressures.
Seat Leakage Test: This test verifies that the valve achieves tight shutoff under pressure, preventing fluid leakage through the seat. Proper seat performance is crucial for isolation and process control.
Dimensional and Visual Inspections: Inspecting valve dimensions, surface finish, and assembly ensures compliance with design specifications and facilitates proper installation. Visual checks also help identify potential defects or damage.
By performing thorough testing and inspections, engineers can ensure valve reliability, extend service life, and prevent costly operational failures.
Marking, Documentation, and Certification
API 600 requires all valves to be clearly marked and properly documented to ensure traceability, quality assurance, and compliance with project and industry standards.
Valve Marking: The body of each valve must be permanently marked with the manufacturer’s name or symbol, pressure class, size, material designation, and serial or heat number. This allows verification of materials, design, and testing throughout the valve’s lifecycle.
Certification and Documentation: Valves must be accompanied by records confirming compliance with API 600 and referenced ASME standards. Required documents typically include material test reports, hydrostatic shell and seat leakage test results, and inspection certificates.
Traceability: All markings and documentation must allow tracking of materials, manufacturing processes, and test history. This is essential for quality control, regulatory compliance, and future maintenance or service requirements.
Practical Guidelines for Valve Selection and Use
Choosing the right valve requires considering service conditions, materials, design features, and system requirements. API 600 provides the framework, but practical decision-making ensures valves perform reliably in the field.
Service Conditions: Evaluate the fluid type, pressure, temperature, and presence of corrosive or erosive substances. This determines the appropriate materials, seat design, and pressure rating for the valve.
Valve Type and Design: Select rising or non-rising stem valves, wedge or parallel discs, and bonnet types based on operating conditions and space constraints. Consider fire-safe or extended bonnet designs for extreme applications.
Material Selection: Ensure the body, bonnet, trim, and sealing materials are compatible with the fluid and temperature conditions. Hard-facing or special alloys may be required for high-pressure, erosive, or high-temperature applications.
Installation and Maintenance: Consider ease of installation, alignment with piping, and future maintenance requirements. Flanged connections are easier to service, while welded connections provide leak-proof performance for critical systems.
By following these practical guidelines, engineers and project teams can select valves that meet operational demands, reduce downtime, and ensure long-term reliability.
Annexes Simplified
API 600 includes several annexes that provide additional guidance for specifying, documenting, and maintaining valves. While the standard can be technical, these annexes can be simplified for practical use.
Annex B – Purchaser-Specified Details: This annex outlines the information the purchaser should provide, such as service conditions, pressure, temperature, and special material requirements. Providing these details ensures the valve meets project-specific needs.
Annex C – Valve Nomenclature: Standardized terminology for valve parts and features simplifies communication between engineers, manufacturers, and procurement teams, reducing errors in specification and documentation.
Annex D – Acceptable Material Combinations: Lists compatible materials for body, bonnet, trim, and seats. Following these recommendations helps avoid corrosion, wear, and compatibility issues, extending valve life.
Annex E – Wear and Travel Monitoring: Describes techniques to measure valve stem travel and monitor wear over time. Regular checks help detect early signs of deterioration and plan maintenance before failures occur.
By understanding these annexes in practical terms, engineers can ensure valves are properly specified, installed, and maintained for reliable operation.
Conclusion
To ensure reliable performance and safety, engineers and project teams should reference API 600 directly when specifying or inspecting bolted bonnet steel gate valves. Focus on selecting the correct valve type, materials, trim, and flanged connections according to your system’s pressure, temperature, and service conditions. Use the standard’s dimensional guidelines, trim tables, and ASME references during design, procurement, and maintenance to minimize operational risks, ensure compliance, and extend valve service life.
