Properties of Ethylene (C₂H₄)
What is Ethylene?
Welcome to a dedicated technical reference for the properties of ethylene (C₂H₄), also known as ethene. This resource is engineered for industry professionals, researchers, and students who require immediate access to validated physical, chemical, and thermodynamic data. The information presented here is critical for process design, equipment specification, and safety planning. You will find key constants, phase behavior charts, and handling guidelines compiled for quick consultation. This page serves as a concise, reliable datasheet to support your engineering calculations and operational decisions.
Molecular Structure & Bonding
- Molecular Formula: C₂H₄
- Structural Formula: H₂C=CH₂
- Bonding: Ethylene consists of two carbon atoms double-bonded to each other, with each carbon also bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
- Hybridization: Each carbon atom is sp² hybridized, forming a trigonal planar geometry.
- Bond Angle: Approximately 120° between H-C-H and H-C=C bonds.
- Pi (π) Bond: The double bond includes one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond, making ethylene reactive in polymerization and addition reactions.
Properties of Ethylene
| Property | Description/Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Properties | ||
| Chemical Formula | C2H4 | - |
| IUPAC Name | Ethene | - |
| Molecular Weight | 28.054 | g/mol |
| CAS Number | 74-85-1 | - |
| Hybridization | sp2 | - |
| Bond Angle | ≈120 | degrees |
| Physical Properties | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | - |
| Odor | Faint sweet/musky | - |
| State at STP | Gas | - |
| Melting Point | -169.2 | °C |
| Boiling Point | -103.7 | °C |
| Density (gas, 15°C) | 1.178 | kg/m³ |
| Density (liquid, b.p.) | 570 | kg/m³ |
| Solubility in Water | 25 | mg/L (25°C) |
| Refractive Index | 1.363 | (at -100°C) |
| Viscosity (gas, 25°C) | 0.0108 | cP |
| Dipole Moment | 0 | D (Debye) |
| Thermal Properties | ||
| Critical Temperature | 9.9 | °C |
| Critical Pressure | 50.4 | bar |
| Critical Density | 214 | kg/m³ |
| Autoignition Temperature | 490 | °C |
| Flammability Limits | 3-36 | % in air |
| Heat of Combustion | -1411 | kJ/mol |
| Heat of Formation | 52.3 | kJ/mol |
| Specific Heat Capacity (gas, 25°C) | 1.53 | kJ/(kg·K) |
| Thermal Conductivity (gas, 25°C) | 0.017 | W/(m·K) |
Phase Behavior, Density Change & Temperature
Understanding ethylene’s phase changes is critical for process design, particularly for operations involving liquefaction, storage, and pipeline transport near its critical point.
The chart below (conceptual) illustrates how the density of ethylene changes with temperature at a fixed pressure (e.g., 50 bar).
Liquid Phase (Blue Region): At temperatures below the critical point (9.9°C / 282.9 K), ethylene exists as a liquid. Density decreases predictably as temperature increases.
Supercritical Phase (Red Region): Above the critical temperature and pressure, ethylene becomes a supercritical fluid, exhibiting properties of both a gas and a liquid. Density drops rapidly and is highly sensitive to changes in temperature and pressure.
Critical Point (Star Marker): The specific combination of critical temperature (9.9°C) and critical density (214 kg/m³) where the distinction between liquid and gas disappears.
Engineering Implications: Systems must be designed to account for the large changes in density and volumetric flow rate that occur through this region. The pressure selector in the original concept allows engineers to model behavior at different operating conditions, which is essential for specifying pump and compressor requirements, vessel sizes, and control systems.
Effect of Temperature on Ethylene Density
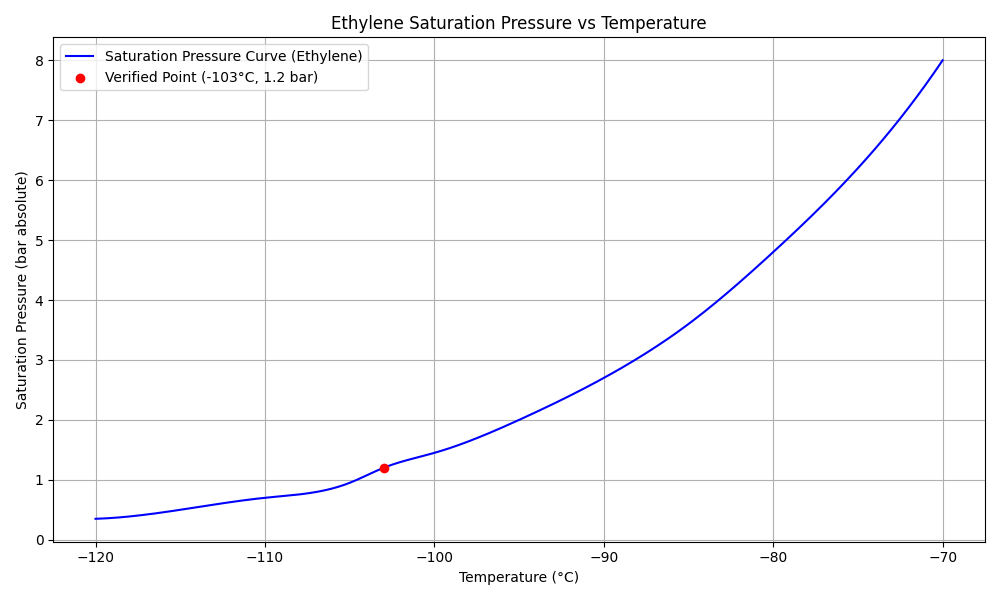
Data Source: NIST Chemistry WebBook and NIST Technical Note 1045
Verified saturation pressure of ethylene at -103°C is approximately 1.2 bar absolute.
Primary Industrial Production
Ethylene is predominantly produced on an industrial scale via steam cracking. In this process, hydrocarbon feedstocks (e.g., naphtha, ethane, propane) are mixed with steam and heated to very high temperatures (750–950 °C) in a furnace for very short durations (milliseconds). This thermal cracking breaks down the large molecules into smaller, unsaturated ones, with ethylene being the primary product.
Major Industrial Applications
Ethylene is a precursor to more complex compounds. Its primary uses include:
Polymers (~60%): Manufacture of polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Chemicals: Production of ethylene oxide (for antifreeze), ethylene glycol, ethanol, and acetaldehyde.
Industrial Gases: Used as a refrigerant and in oxy-ethylene welding and cutting.
Agriculture: Used in a controlled manner to ripen fruits.
Safety & Handling
Hazards: Extremely flammable gas. Forms explosive mixtures with air. Acts as a simple asphyxiant by displacing oxygen. Although not highly toxic, it can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and unconsciousness in high concentrations.
Leak & Fire Response: Eliminate ignition sources. Stop leak if safe to do so. Use water spray to keep exposed containers cool and to disperse vapors.
Storage & Handling: Store in a well-ventilated, cool, dry area away from direct sunlight, heat, and oxidizers. Use equipment rated for its pressure and service. Ground and bond containers during transfer.
Related Resources
Check out other useful pages !