Pumps: Types, Applications & Selection Guide
A pump is a mechanical device designed to move fluids from one place to another by creating pressure or suction. It works by converting mechanical energy, typically from an electric motor or engine, into hydraulic energy, which forces the fluid through a piping system. Pumps operate using different mechanisms depending on their type i.e., centrifugal pumps use a rotating impeller to create flow, while positive displacement pumps trap fluid in a chamber and force it out with pistons, gears, or diaphragms. Pumps are essential in various applications, including water supply, industrial processes, and chemical handling, ensuring efficient fluid transfer and pressure control.
Pumps are optimized for incompressible fluids (liquids), compressors and fans are the equivalent machines used for gases, since gases behave differently under pressure.
However, there are a few exceptions where pumps interact with gases:
- Vacuum pumps remove gas from an enclosed space to create a partial vacuum.
- Certain specialized pumps can handle gas-liquid mixtures in industrial processes.
For most practical purposes, though, pumps = liquids, compressors/fans = gases. The key difference lies in compressibility i.e., gases can be squeezed (compressed), while liquids cannot.
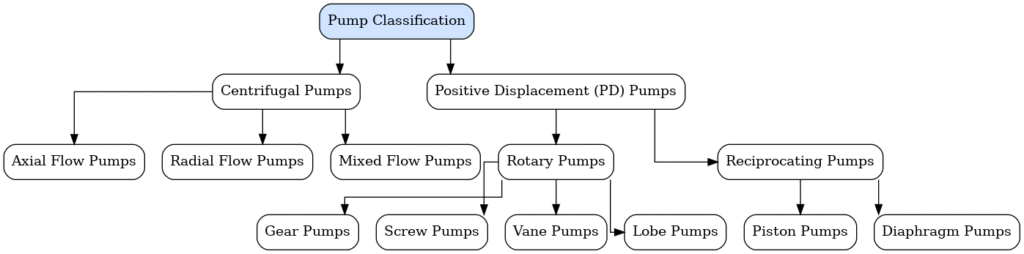
Classification of Pumps
1. Centrifugal Pumps
How They Work: A centrifugal pump operates by converting rotational energy from an impeller into kinetic energy in the fluid, which is then transformed into pressure energy to move the liquid. The process begins when the pump’s motor spins the impeller at high speed, creating centrifugal force that flings the liquid outward from the impeller’s center to its edges. As the liquid exits the impeller, it enters the volute (a spiral-shaped casing), where its velocity decreases, increasing its pressure due to the conservation of energy. The pressurized liquid is then discharged through the outlet pipe, while low pressure at the impeller’s center draws more fluid in through the suction inlet, ensuring continuous flow. Centrifugal pumps are efficient for low-viscosity liquids and are widely used in water supply, irrigation, and industrial applications due to their simplicity, smooth flow, and ability to handle high flow rates.
Applications of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are extensively used across multiple industries for fluid handling. In Water Utilities, they supply drinking water and manage sewage treatment. Oil & gas refineries use them for crude transfer and cooling systems, while Power Plants rely on them for coolant circulation. Agriculture employs these pumps for irrigation and drainage, and HVAC systems utilize them for chilled water circulation. Food & Beverage plants apply them in milk/beverage processing, and Marine operations use them for ballast/bilge pumping. Mining depends on centrifugal pumps for dewatering and slurry transport. Their high-flow, low-maintenance design makes them ideal for moving low-viscosity fluids efficiently.
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps
- Simple Design & Easy Maintenance – Fewer moving parts compared to positive displacement pumps, reducing wear and repair costs.
- Smooth, Continuous Flow – Provides steady, non-pulsating liquid discharge, ideal for sensitive processes.
- High Flow Rates – Efficient for moving large volumes of low-viscosity liquids (e.g., water, thin oils).
- Compact & Lightweight – Takes up less space than many other pump types.
- Handles Contaminated Liquids – Can pump liquids with small solids (if designed with open or semi-open impellers).
- Energy Efficient at Optimal Conditions – Consumes less power when operating near its best efficiency point (BEP).
Limitations of Centrifugal Pumps
- Not Self-Priming – Requires the pump casing to be filled with liquid before starting; may need additional priming systems.
- Struggles with High-Viscosity Liquids – Efficiency drops significantly with thick fluids (e.g., syrups, heavy oils).
- Sensitive to Air/Gas Entrainment – Presence of gas bubbles can cause cavitation, reducing performance.
- Limited Pressure at Low Flow – Pressure generation depends on speed; cannot achieve high pressures like positive displacement pumps.
- Performance Varies with Speed – Flow and pressure are highly dependent on impeller speed (fixed by laws of affinity).
- Not Ideal for Precise Metering – Flow rate changes with system pressure, making it unsuitable for exact dosing applications.
2. Reciprocating (Positive Displacement) Pumps
How They Work: Positive displacement (PD) pumps operate by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and mechanically forcing it into the discharge pipe, creating a consistent flow regardless of pressure. Unlike centrifugal pumps, PD pumps use reciprocating or rotating mechanisms—such as pistons, gears, lobes, or diaphragms—to physically displace the fluid. In reciprocating types (e.g., piston or diaphragm pumps), a back-and-forth motion expands and contracts a cavity to draw in and expel fluid. In rotary types (e.g., gear or screw pumps), rotating components transfer fluid from the suction to the discharge side with minimal slippage. Since PD pumps seal and move discrete amounts of fluid, they excel at handling high-viscosity liquids (e.g., oils, slurries) and provide precise flow control, making them ideal for dosing, high-pressure applications, or systems where suction lift is required. However, they require relief valves to prevent overpressure damage due to their constant displacement nature. Their efficiency remains high even at low flow rates, but they generally have higher maintenance needs due to mechanical wear.
Applications of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps are widely used in industries requiring precise fluid handling, high-pressure delivery, or viscous fluid transfer. In the oil and gas industry, they are essential for chemical injection systems, such as metering pumps that precisely dose additives into pipelines. The food and pharmaceutical sectors rely on sanitary lobe pumps for transferring viscous products like yogurt or syrup without contamination. In wastewater treatment, progressive cavity pumps handle sludge and abrasive slurries efficiently. The chemical industry uses diaphragm pumps to safely transfer corrosive or hazardous liquids, while hydraulic systems in manufacturing depend on gear pumps to maintain precise oil pressure. For high-pressure applications like water jet cutting, intensifier pumps deliver ultra-high-pressure water streams. These pumps are chosen for their ability to maintain flow accuracy, handle thick or sensitive fluids, and operate under demanding pressure conditions where centrifugal pumps would fail.
Advantages of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement (PD) pumps offer several key benefits that make them indispensable for specialized industrial applications. Their ability to deliver a constant flow rate regardless of pressure changes ensures precise metering, critical in chemical dosing or fuel injection systems. Unlike centrifugal pumps, PD pumps excel at handling high-viscosity fluids like heavy oils, slurries, or pastes, as seen in food processing (e.g., chocolate transfer) or wastewater sludge pumping. They provide superior suction lift capabilities, enabling self-priming in applications like tanker truck unloading or remote fluid transfer. PD pumps also achieve higher pressure outputs—gear pumps in hydraulic systems, for instance, can sustain thousands of psi. Their efficiency remains high at low speeds and variable flow rates, making them ideal for batch processes in pharmaceuticals or paint production. Additionally, certain designs (e.g., diaphragm pumps) handle abrasive or shear-sensitive fluids without damage, crucial for mining slurries or biotechnology. While maintenance demands are higher, their reliability in extreme conditions justifies their use where centrifugal pumps would fail.
3. Screw Pumps (Progressive Cavity & Twin-Screw)
How They Work – Screw pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that use one or more rotating screws (helical rotors) to move fluid axially along the screw threads with minimal turbulence. As the screws rotate within a tightly fitted casing, they create sealed cavities between the screw flights and the pump housing. These cavities trap the fluid at the suction inlet and progressively push it toward the discharge end in a smooth, continuous flow. The intermeshing screws prevent backflow, ensuring consistent pressure and efficiency even with viscous or abrasive fluids. Twin-screw designs (with two parallel screws) are common for high-pressure applications like fuel oil transfer or polymer extrusion, while triple-screw pumps excel in lubrication systems for heavy machinery due to their pulsation-free output. Their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities—from thin solvents to thick asphalt—with low shear forces makes them ideal for marine hydraulics, crude oil pipelines, and food processing (e.g., chocolate or peanut butter pumping). Unlike centrifugal pumps, screw pumps maintain efficiency across varying pressures and flow rates, though they require precise manufacturing to minimize internal leakage.
Advantages of Screw Pumps
Screw pumps offer several distinct benefits, making them a preferred choice for demanding industrial applications. Their high efficiency and consistent flow rate, even under varying pressures, ensure reliable performance in processes like fuel transfer, lubrication systems, and hydraulic operations. Unlike centrifugal pumps, screw pumps excel at handling high-viscosity fluids (e.g., heavy oils, syrups, or asphalt) without losing efficiency, while their low-shear operation preserves the integrity of shear-sensitive materials like polymers or food products (e.g., chocolate or yogurt). The pulsation-free flow minimizes vibration and noise, which is critical in precision applications such as marine hydraulics or chemical dosing. Additionally, screw pumps are self-priming and can handle gas-liquid mixtures, making them ideal for crude oil pipelines or wastewater treatment. Their robust design allows for long service life with minimal maintenance, even when pumping abrasive or corrosive fluids. These advantages make screw pumps indispensable in industries requiring precise, high-pressure fluid transfer with minimal turbulence or degradation.
Industrial Application of Screw Pumps
Screw pumps are widely used across industries due to their ability to handle viscous, abrasive, and sensitive fluids with high efficiency. In the oil and gas industry, they are employed for crude oil transfer in pipelines, where their self-priming capability and tolerance for gas-entrained fluids ensure uninterrupted flow. The marine industry relies on screw pumps for fuel oil transfer aboard ships, as they maintain steady pressure and handle varying fuel viscosities. In food processing, triple-screw pumps are used for chocolate pumping, as their gentle, low-shear action preserves texture and prevents separation. The chemical industry utilizes them for polymer transfer, where precise metering and resistance to abrasive additives are critical. Wastewater treatment plants deploy screw pumps for sludge dewatering, as they efficiently move thick, solids-laden fluids without clogging. Each application leverages the pump’s ability to deliver consistent flow, handle challenging fluids, and operate under demanding conditions.
4. Gear Pumps
How They Work: Gear pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that use intermeshing gears to move fluid through the pump housing. As the gears rotate, fluid is trapped in the spaces between the gear teeth and the pump casing, creating a sealed chamber. The fluid is carried from the suction (inlet) side to the discharge (outlet) side, where the meshing of the gears forces the fluid out under pressure. External gear pumps, with two identical gears, are common for high-pressure applications, while internal gear pumps, with a rotor and idler gear, excel in handling viscous or shear-sensitive fluids. The tight tolerances between the gears and casing minimize slippage, ensuring efficient and consistent flow even with varying pressures.
Application of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps offer several key advantages, including their compact and simple design, which makes them easy to install and maintain. They provide high-pressure output and precise flow control, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate fluid metering, such as lubrication systems or hydraulic power units. Their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities, from thin solvents to thick oils, without losing efficiency makes them versatile across industries. Gear pumps are also self-priming and can operate in both directions, adding to their flexibility. Additionally, they generate minimal pulsation, ensuring smooth and quiet operation, which is critical in precision applications like fuel injection or chemical dosing.
Advantages of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are widely used in industries requiring reliable and efficient fluid transfer. In the automotive sector, they are essential for engine lubrication systems, where they ensure consistent oil flow to critical components. The chemical industry relies on gear pumps for transferring resins, adhesives, and solvents, thanks to their resistance to corrosive fluids and precise flow control. In food and beverage processing, gear pumps handle molasses, syrups, and cooking oils, where their gentle pumping action preserves product quality. Hydraulic systems in manufacturing and construction use gear pumps to power machinery, as they deliver high-pressure fluid with minimal energy loss. These examples highlight the pump’s versatility in handling diverse fluids and operating conditions.
Key Selection Criteria for Pumps in Industry
1. Fluid Characteristics
- Viscosity: Centrifugal pumps for thin fluids (<500 cP); PD pumps (gear, screw) for thick fluids (oils, slurries).
- Abrasiveness: Slurry pumps with hardened materials for solids; peristaltic pumps for abrasive fluids.
- Corrosivity: Material compatibility (e.g., stainless steel, PTFE-lined for acids).
- Temperature: High-temp designs for steam/thermal oils.
2. Flow Rate & Pressure Requirements
- High flow, Low Pressure: Centrifugal pumps (e.g., cooling water systems).
- Low flow, High Pressure: PD pumps (e.g., piston pumps for water jet cutting).
- Pulsation Sensitivity: Rotary PD pumps (lobe, gear) for smooth flow.
3. System Conditions
- Suction Lift: Self-priming pumps (diaphragm, screw) for dry starts.
- NPSH Available: Centrifugal pumps require adequate NPSHa to avoid cavitation.
- Continuous vs. Intermittent Duty: Seal/bearing durability for 24/7 operation.
4. Energy Efficiency
- Match pump to Best Efficiency Point (BEP): variable speed drives (VFDs) for fluctuating demands.
- PD pumps maintain efficiency across pressures; centrifugals lose efficiency at low flow.
5. Maintenance & Lifecycle Costs
- Seal Type: Mechanical seals (low leakage) vs. packed seals (repairable).
- Accessibility: Split-case designs for easy maintenance.
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures): Robust designs (e.g., mag-drive pumps) for hazardous fluids.
6. Industry-Specific Needs
- Food/Pharma: Sanitary pumps (3A-compliant, CIP-capable).
- Oil/Gas: API 610 pumps for refineries.
- Mining: Abrasion-resistant slurry pumps.
7. Compliance & Standards
- Explosion-proof motors (ATEX, NEC) for flammable environments.
- Hygienic Certifications (EHEDG, FDA) for food processing.
Quick Decision Guide
| Scenario | Pump Type |
|---|---|
| High flow, clean water | Centrifugal |
| Precision chemical dosing | Diaphragm/Peristaltic |
| High-viscosity oil | Screw/Gear |
| Slurry with solids | Progressive Cavity |
8. Industry-Specific Pump Selection Guidelines
Industry-Specific Pump Selection Guidelines ensure optimal performance, safety, and compliance by tailoring pump choices to unique operational demands. In oil & gas, API 610-certified centrifugal pumps with dual seals prevent hydrocarbon leaks, while chemical plants prioritize corrosion-resistant materials like PTFE-lined or Hastelloy pumps for acids. Food/pharma mandates sanitary 316L stainless steel lobe pumps with CIP compatibility, and mining relies on rubber-lined slurry pumps for abrasive fluids. Power plants use multistage centrifugal pumps for high-pressure boiler feed, and water treatment favors non-clogging vortex designs. Each industry balances standards (API, ASME, 3A), fluid properties, and lifecycle costs to avoid failures and downtime.
Here’s a comprehensive, full-length technical article on Energy Efficiency & Cost Analysis in Pump Selection, suitable for engineers and professionals in industries such as oil & gas, water treatment, and manufacturing.
Energy Efficiency & Cost Analysis in Pump Selection
Pumps are integral components in countless industrial systems, transporting fluids in processes ranging from water treatment to chemical manufacturing. With global emphasis on sustainability and operational cost optimization, selecting an energy-efficient pump is no longer optional—it’s essential. Proper pump selection not only ensures process reliability but also reduces lifecycle costs significantly. This article delves into the principles of energy efficiency in pump selection and explores how to perform a cost analysis that justifies investment decisions.
Understanding Pump Efficiency
Pump efficiency is defined as the ratio of hydraulic power delivered to the fluid (output) to the mechanical power supplied to the pump shaft (input). It is expressed as:

High efficiency translates to less energy loss and lower electricity costs. Efficiency varies with the operating point; most pumps are designed to be most efficient at the Best Efficiency Point (BEP).
Lifecycle Cost Components
1. Initial Costs
- Purchase of the pump and motor.
- Installation (foundation, piping, alignment).
2. Operating Costs
- Energy consumption (largest component over time).
- Maintenance and repair.
- Downtime and loss of productivity.
3. Disposal Costs
Decommissioning and material recycling at the end of service life.
A well-conducted lifecycle cost (LCC) analysis helps quantify total expenses over the pump’s operational life:
Pump Selection Criteria for Efficiency
1. Match Operating Point to BEP
Always select a pump whose BEP is as close as possible to the system’s duty point. Operating too far from BEP results in:
- Higher energy use
- Increased vibration
- Premature wear
2. Avoid Oversizing
Oversized pumps lead to throttling losses and inefficient operation. Consider:
- Variable speed drives (VSDs) for varying demands
- System curve analysis for accurate sizing
3. Consider System Design
Reduce losses in:
- Piping (friction losses)
- Valves and fittings
- Elevation head
Optimizing the system may allow for a smaller, more efficient pump.
Case Study: Cost Comparison
Scenario: Two pumps selected for the same application.
| Parameter | Pump A (Standard) | Pump B (High-Efficiency) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 65% | 75% |
| Power Required | 100 kW | 86.7 kW |
| Electricity Rate | $0.10/kWh | $0.10/kWh |
| Operating Hours/Year | 4,000 | 4,000 |
| Energy Cost/Year | $40,000 | $34,680 |
| Initial Cost | $15,000 | $20,000 |
| Payback Period | — | < 1 year |
Though Pump B has a higher initial cost, the payback period is less than a year due to energy savings.
Conclusion
Selecting the right pump with energy efficiency in mind is one of the most effective ways to reduce operational costs and minimize environmental impact. A lifecycle cost approach offers a holistic view that goes beyond initial investment, helping stakeholders justify choices that deliver long-term benefits.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
To know about maintenance best practices, trouble shooting, failure issues and performance monitoring. Refer maintenance section of the website. Click Here
Industry Standards for Pumps
API 610 – (Centrifugal Pumps for Petroleum Industry)
API 674 – (Reciprocating Pumps)
ISO 13709 – (Petroleum Pump Specifications)
To know more about Codes & Standards for process industry, refer codes & standards section of the website. Click Here